

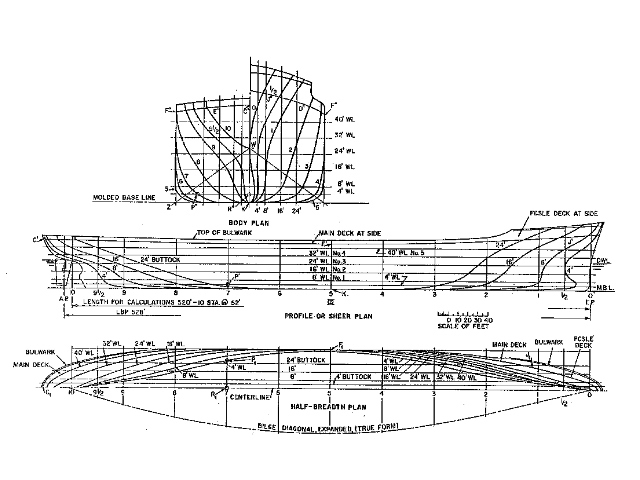
Fore and aft translation is termed surge.While atop a liquid surface a floating body has 6 degrees of freedom in its movements, these are categorized in either rotation or translation. Ship motions – involves motions of the vessel in seaway and its responses in waves and wind.Ĭontrollability (maneuvering) – involves controlling and maintaining position and direction of the vessel. Some vessels are electrically powered using nuclear or solar energy. Engine types are mainly internal combustion. Propulsion – to move the vessel through water using propellers, thrusters, water jets, sails etc. Powering calculation is done based on this. Resistance – resistance towards motion in water primarily caused due to flow of water around the hull. Hydrodynamics concerns the flow of water around the ship's hull, bow, and stern, and over bodies such as propeller blades or rudder, or through thruster tunnels. This involves computing buoyancy, displacement, and other hydrostatic properties such as trim (the measure of the longitudinal inclination of the vessel) and stability (the ability of a vessel to restore itself to an upright position after being inclined by wind, sea, or loading conditions). Hydrostatics concerns the conditions to which the vessel is subjected while at rest in water and to its ability to remain afloat. Naval architecture also involves formulation of safety regulations and damage-control rules and the approval and certification of ship designs to meet statutory and non-statutory requirements.īody plan of a ship showing the hull form Ship design calculations are also required for ships being modified (by means of conversion, rebuilding, modernization, or repair). Preliminary design of the vessel, its detailed design, construction, trials, operation and maintenance, launching and dry-docking are the main activities involved. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation (classification) and calculations during all stages of the life of a marine vehicle. Naval architecture, or naval engineering, is an engineering discipline incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the engineering design process, shipbuilding, maintenance, and operation of marine vessels and structures. General Course of Study leading to Naval Architecture degree


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
